Plastic 3D printing technologies: HP Multi Jet Fusion vs SLS
Posted By Amandine Richardot on Aug 22, 2017 | 2 comments
According to our 2017 study The State of 3D printing, plastic is still the most used 3D printing material. At Sculpteo, we used to 3D print your plastic parts using the SLS technology (Selective Laser Sintering), but a few weeks ago we started offering you a new option to match more precisely your needs. This new plastic 3D printing technology called Multi Jet Fusion was created by HP. What are the differences between these two technologies? Which one shall you use for your project? Here are our answers!
Introducing both of these plastic 3D printing technologies
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is the most used 3D printing technology at Sculpteo. It’s mostly used by professional companies and online 3D printing services. Indeed, SLS 3D printers are usually quite large and expensive.
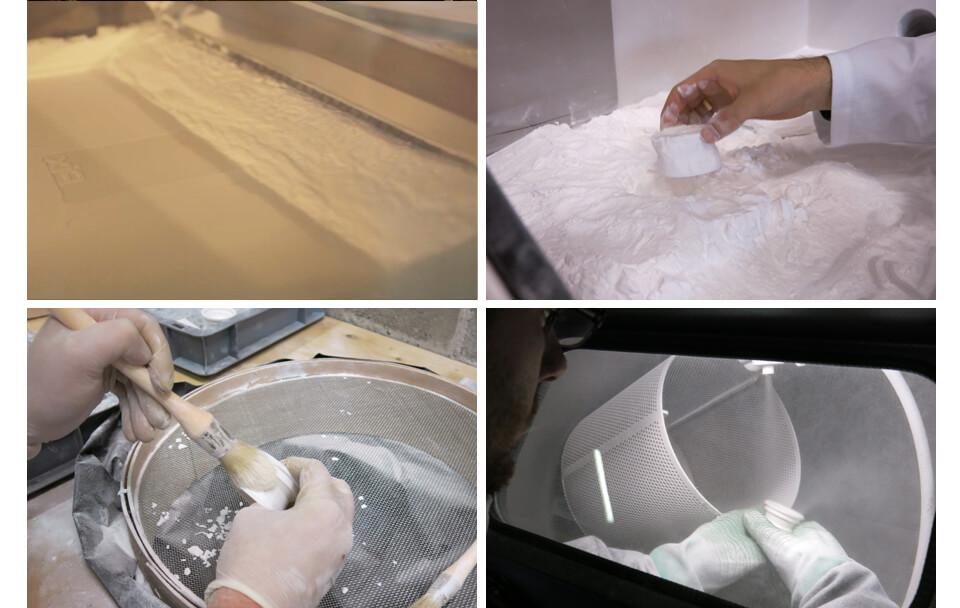
How does it work? A powder is deposited on the build stage. Then, a laser selectively scans this thin layer of powder, sintering the powder particles together according to the shape desired for this precise layer of the design. Afterwards, the build platform is lowered one layer down, and the whole process starts once again until the 3D printed part is complete.
Once this whole process is done, the completed object is removed from the 3D printer and it’s depowdered. No further process is necessary, except if you choose any additional finish (paint, polishing, dye, smoothing beautifier…).
SLS doesn’t require supports since the powder acts as a self-supporting material. It allows the construction of intricate and complex geometries, and thus an almost total design freedom.
HP Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
HP Multi Jet Fusion is a 3D printing technology which is quite similar to Binder Jetting. Indeed, it uses a liquid binding agent in order to create the different layers of your 3D printed part. Once this agent is deposited on the powder bed, a detailing agent is also deposited in order to get the finest details and a smooth surface.
This 3D printing process needs less heat to fuse the powder than SLS. It still needs to cool once the part is ready, but it goes way faster. At that point, the building box is placed into the post-processing station which cools the parts and makes them ready for cleaning. Once depowdering is done, your object is ready.
Which plastic 3D printing technology should you choose?
HP Multi Jet Fusion for more precise 3D printed parts
One of the most interesting things that can be achieved thanks to the HP Multi Jet Fusion technology is high precision. Parts 3D printed using the SLS technology are also really precise, but the detailing agent used in the Multi Jet Fusion process takes precision to the next level. As a result, your parts can be extremely precise, with complex designs.
Moreover, layer thickness with this plastic 3D printing technology is of 80µm, whereas it can go up to 100µm with the SLS technology. This also brings a higher level of precision to your parts.
SLS for more choice in terms of materials, colors and finishing options
Since the HP Multi Jet Fusion was launched quite recently, it only offers Black PA12 parts, with no finishing options available. The result is already satisfying without finishes, that’s why this 3D printing process can be chosen even to make finished products. But you might want to have more choice regarding your object. If it’s the case, SLS can be the right technology for you.
Indeed, SLS offers you a large range of materials: PA12 Plastic (Nylon), Alumide, CarbonMide, Glass-Filled Nylon and PEBA (Flexible Plastic). Thus, you can find a 3D printing plastic which totally matches your needs, either if you want to create a flexible plastic part or an extremely strong one.
Moreover, many coloring and finishing options are available, even just for PA12 (the most used 3D printing plastic material). For instance, you can use the exclusive finish we developed at Sculpteo: the Smoothing Beautifier. This physicochemical process makes the surface of your object glossy and incredibly smooth, which is great for finished products.
Now, you know how to choose between these two plastic 3D printing technologies. Once you’ve made up your mind, upload your 3D model on our 3D printing service!
Are you hesitating between other 3D printing technologies? Discover our blog post comparing SLS, SLA, CLIP and FDM!


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook