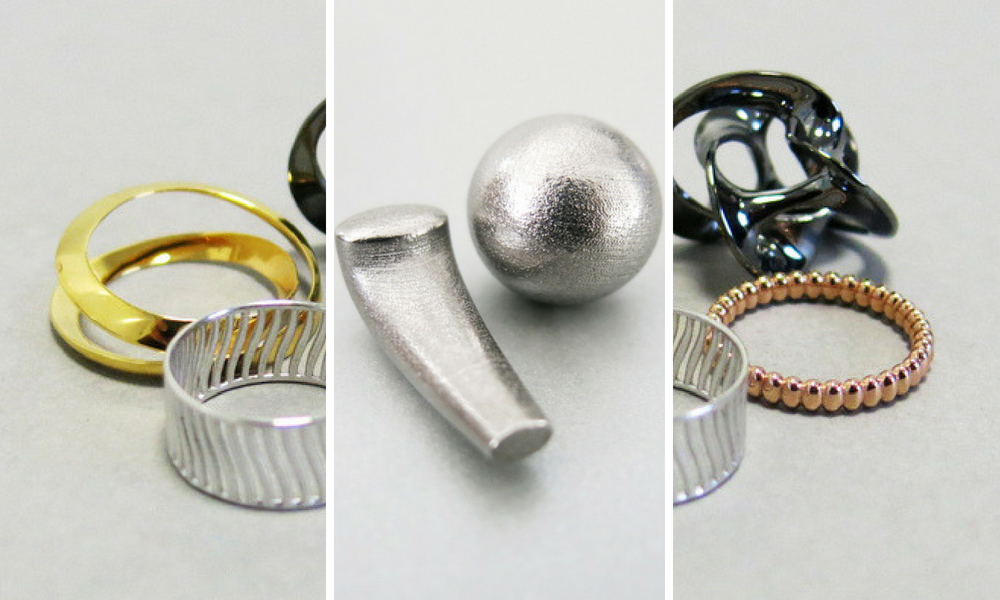3D printing materials: Which metal should you choose for your project?
Posted By Kat Plewa on Jul 23, 2018 | 0 comments
Choosing Additive Manufacturing for your production can be just what your business needs right now. 3D printing provides you with a large amount of techniques and possibilities and can be used in numerous industries, from implants created with bioprinting to 3D printed tires. In this blogpost, we’ll focus on metal materials used in 3D printing, some of which have high-temperature resistance, good mechanical properties for the aerospace appliance or great characteristics for a more decorative use. Moreover, we prepared for you an overview of our 3D printing services for metals. Learn how you can use 3D printed metals for your production now, and which 3D printing material is the best for your project!
An overview of metal 3D printing technologies
Deciding which 3D printing technology to use might be tough, but it’s the most important step to assure your 3D printed object will meet your expectations. We suggest you start from the end result: what properties your final product needs to have. Listing those will help you see what exactly your 3D printed model needs to feature.
Knowing which of your metal print’s properties are essential will make it easier for you to see which of our metals will suit your desires best. Here are the additive manufacturing technologies available on our 3D printing service: Selective Laser Melting, Direct Metal Laser Sintering, Binder Jetting, and Casting. See how easy it is!
Selective Laser Melting
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is a 3D printing technology based on laser melting. The metal powder is placed on the bed of the 3D printer layer by layer and the laser beam is sintering the shape of your 3D model on each layer. 3D printing technology is good for pure metals such as titanium or aluminum. SLM is perfect for prototyping, as it’s quick. It’s also detailed and can be used to integrate multiple components into a single object, and the obvious benefits from that are lower costs and faster production as there is no need for assembling the parts.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) technology works just like SLM, the printer applies one layer of 3D printing material, and the laser melts the metal accordingly to the shape of your 3D model. The difference is that DMLS doesn’t fully melt the powder like the SLM printer does. The consequence of that is that metal prints made with DMLS 3D printing technology don’t need to reach a temperature as high and therefore the cooling time is shorter. DMLS is perfect for low- volume production as it eliminates time- consuming tooling. It’s also a great solution for prototyping as it provides highly detailed designs.
Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting is an Additive Manufacturing method which uses production principles that differ from SLM and DMLS. The 3D printer spreads a layer of powder metal, then it uses a liquid binding agent to harden the powder in the shape of your 3D model. For better solidification, the 3D printing material is lightly cured between each layer. When the 3D printing process is finished, your part is placed in an oven for curing.
The last part of this 3D printing technique is to clean the metal print of the remaining powder with air blowers and brushes. Binder Jetting is the fastest and cheapest metal 3D printing method. It also provides a high level of details. If you are looking for an affordable and quick method for prototyping, or a technique to create ornamental and decorative objects such as jewelry, this is the right choice for you. Binder Jetting will let you achieve high customization in a short amount of time. However, if your parts need to handle a fair amount of stress, we suggest SLM or DMLS as a better fit for your needs.
Casting
Lost- Wax Metal Casting unlike mentioned above Additive Manufacturing methods is based on 3D printing a perfect wax model of your object, building plaster mold around it and then injecting liquid metal, which pushes out the wax through a treelike structure to create your 3D model. Casting lets you achieve a high level of custom made and complex objects, with very smooth surface and sharp edges if needed. This 3D printing method is mostly used for jewelry production.
Which of our metals for 3D printing is best for your project?
One of our 3D printing materials Aluminum AlSi7Mg0.6 is printed with the SLM technology. It’s a fine metal powder containing mostly aluminum (>90%), silicone (7%) and magnesium (0.6%). The main characteristics for this 3D printing metal are good mechanical properties, durability, and lightweight, which makes it a good material for production.
Aluminum AlSi7Mg0.6 is especially good if your parts have to have good thermal properties and if they require good strength/ mass ratio. This material has good mechanical properties and can be used for parts subject to high voltages. Its composition makes it very suitable for molding. This alloy is commonly used in foundries for fine objects and complex geometries. Originally your 3D metal prints will have a rough surface, but at Sculpteo we provide you with the best service, so contact our sales team to learn about our finishing options.
Stainless Steel 316L (DMLS)
At Sculpteo we have two 3D printing materials available with the DMLS technology. For your 3D metal prints, we offer you Stainless steel 316L and Titanium 6AI-4V. Let’s start with Stainless steel 316L which is composed of iron (66%- 70%), garnished with chrome (16%- 17%), nickel (11%- 14%) and molybdenum (2%- 3%). This 3D printing metal has great mechanical properties such as resistance against corrosion and is distinguished for its high ductility.
Thanks to the addition of chrome in Stainless steel 316L, the 3D printing metal doesn’t really attract dirt which gives it an amazing opportunity to be used in the medical industry. It’s also a perfect fit for the automobile industry for corrosion-resistant parts, for the aerospace industry to produce mechanical parts, as well as for jewelry and watchmaking to create customized parts.
Titanium 6AI- 4V
Titanium 6AI-4V is made out of Titanium (88%- 90%), Aluminum (5.5%- 6.5%) and Vanadium (3.5%- 4.5%). This 3D printing metal has some amazing features: it has a very low toxicity, but the high melting point (1660°C/ 3260°F), which makes it perfect for different industries, for instance in medicine for bioimplants, military applications, but also in the aerospace and automotive fields. You metal print made with this material will stay perfectly fine when exposed to very right temperature.
Your metal print will also stand out with its strength and high resistance to oxidation and acid. Titanium 6AI-4V not only has some brilliant mechanical properties, it’s also very lightweight! The surface of your metal print will have an average roughness, but to give you the best experience, we offer you numerous polishing options.
Steel/ Bronze 420SS/BR
The last method for layer by layer 3D printing is Binder Jetting. With this 3D printing technology, we offer you a choice of two materials: Steel/ Bronze 420SS/BR and Stainless Steel 316. The 3D printing metal Steel/ Bronze 420SS/BR is made of a fine stainless steel 420 powder, infiltrated with bronze. This infiltration of bronze adds strength and resistance to your metal print.
The final object will then contain 60% stainless steel and 40% bronze. To make it even better we offer polishes to remove any imperfections and a plating variant: Nickel or Gold depending on your needs. This metal is perfect if you need to create ornamental parts at a good price. For models which have to resist more stress we recommend you to use DMLS Stainless Steel.
Stainless Steel 316L (Binder Jetting)
Second of materials used in 3D printing with Binder Jetting method is Stainless Steel 316. Compared to Steel/ Bronze 420SS/BR this metal has a strong resistance against corrosion and high- temperature resistance. These features will make your metal prints great for tooling, molds, or to design parts for the consumer goods sector. With Stainless Steel 316 our production team can polish the object to give it high shine according to your needs.
Bronze
Designing belt buckles of watches? For smaller and objects of ornamental use, we highly suggest you to use Lost Wax Casting. With this 3D printing technology, you can find three metals: Bronze, Brass, and Silver. The most affordable choice is Bronze which is made of copper (90%) and tin (10%). This 3D printing material has a better resistance to tarnish than brass alloys. Bronze also has a harder surface and doesn’t get oxidized. If that’s not enough add to it our Standard 14K color finish!
Brass
If you’re looking for a more delicate look of your metal print, we offer Brass composed of 80% copper, 15% zinc and 5% tin. Your 3D printed model will be solid, but susceptible to scratching and tarnishing when exposed to air, just like any other brass product from a mass production jewelry store. But to protect your 3D printed model we offer you a series of platings such as gold, rose gold white or black rhodium platings. This will give your 3D printed part a great aspect.
Silver
Last but not least, our Silver material for Casting. Made of 92.5% sterling silver and 7.5% of a metal alloy, silver is a great competition to sterling silver products made with commercial production. Thanks to 3D printing and our polishing options you can get highly detailed parts, and beautiful results with your 3D model.
Introducing Additive Manufacturing to your production might be a revolutionary step. The variety of materials and 3D printing technologies is amazing, no matter if you would like your metal print to be a strong and high-temperature resistant prototype or a beautiful and delicate ring. Make sure you know what properties your 3D printed object should have and upload your 3D model today!


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook