The future of 3D printed meat: space steaks
Posted By Kat Plewa on Oct 30, 2019 | 0 comments
There is more and more news when it comes to 3D printing food coming up every day. It seems like a true possibility that in the near future we will be able to grow our food, even meat, thanks to 3D printing. This solution will not only help the animals but also the environment. What is so beneficial about 3D printing meat and why is space the right place to produce 3D printed steaks? Let’s find out!
What are the advantages of 3D printing meat?
In the past, we took a look at burgers produced in labs or 3D printed vegan meat. The problem with them is that they don’t really resemble meat. But the technology is constantly improving and it can still provide us with many benefits.
First of all, we eat to give our body the needed energy and nutrition. As 3D printed meat can be customized, it can provide us with all the proteins we need, and only those. It is true that many animals are fed antibiotics to prevent diseases, but that means we also eat them. With 3D printed meat, we will have antibiotics-free meat.
Additionally, we use up to 15 000 liters of water per 1 kg of produced meat! Conventional meat production is wasting many resources and water is one of the main. We can avoid that if we produce meat with Additive Manufacturing. 3D printing meat uses much less water.
If we reduce antibiotic production, the usage of water and packaging of the meat, we will dramatically lower the emission of pollution. That, of course, leads to global warming. In fact, the food industry is responsible for 37% of global greenhouse-gas emissions. If we 3D print meat, we can enjoy our meals without leaving a devastating environmental footprint.
And an obvious benefit is of course to save the animals. Slaughter-free meat is possible. Some solutions are fully vegan, others use meat cells to grow them and use the material as a 3D printing filament to produce real meat. Let’s have a closer look at how the latter solution works.
In the pursuit of meat’s texture
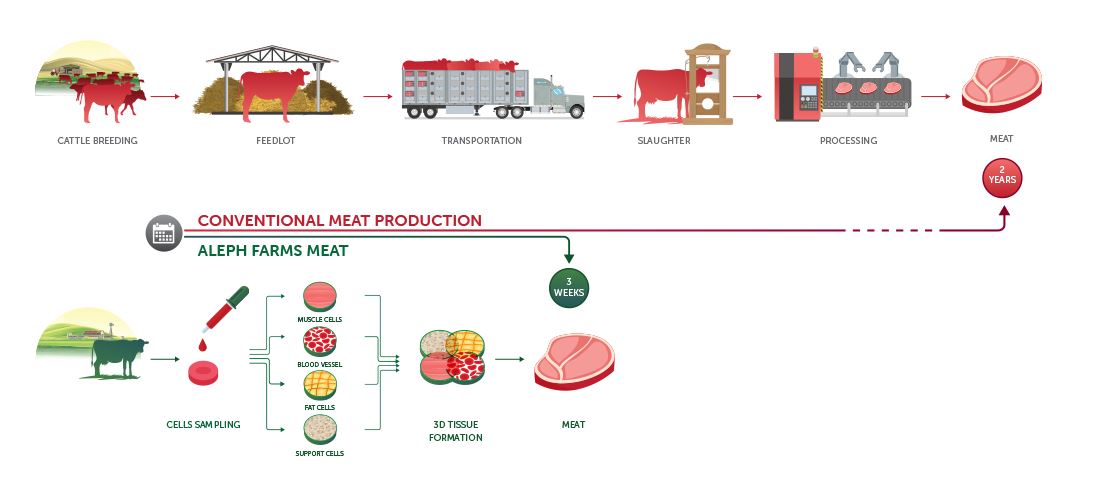
Aleph Farms is an Israeli start-up proudly calling themselves meat growers. They are working with beef and through research and development, they were able to produce a steak in space. The material is taken from a small biopsy from a cow and consists of muscle cells, blood vessels, fat cells, and support cells. Combined they form 3D tissue.
Aleph’s CEO and co-founder, Didier Toubia, explains: “We’re the only company that has the capacity to make fully-textured meat that includes muscle fibers and blood vessels — all the components that provide the necessary structure and connections for the tissue”.
One would ask, why produce the meat in space? Because of gravity. Earth’s gravity is hard to work with when it comes to bio 3D printing. Here, the Additive Manufacturing process requires lattice structures to hold the material. However, in space, zero gravity allows for effective meat 3D printing without any support as it can be built.
The space steak is called by Aleph ‘’minute steak’’ because it only takes a few minutes to cook. At the moment, we’re able to produce thin pieces of steak. The 3D printed meat has the structure and texture of meat cut from a cow. It is also much faster to produce as the graph below shows.
The start-up had a breakthrough just late last year when Russian astronauts managed to produce first-ever 3D printed space steak. Their innovative solution allowed them to use much less water, power, and materials.
What is next for 3D printed meat?
It’s a huge development that Aleph delivered. Hopefully, we’re looking at a future where no animals are harmed and we can produce the full of nutrition meat in a matter of days. There is definitely a huge potential for bio 3D printing, not only in the food industry but also for medical applications such as 3D printing organs, drug testing for cosmetics and new treatments or bone tissue regenerations.
If you have a 3D printing project, don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to help you get it produced at the best quality possible. And it’s ready, simply upload your file to our online 3D printing service!
And don’t forget to subscribe to our Newsletter and follow us on Facebook to get a dose of the latest 3D printing news!


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook