Rotational 3D printing: A new technology for stronger parts
Posted By Lucie Gaget on Sep 21, 2018 | 0 comments
New 3D printing techniques are unveiled quite regularly. Indeed, this cutting-edge technology fascinates researchers around the world, and new discoveries are made leading to innovative applications in various sectors such as medical or architecture.
Today, we are going to tell you about a new 3D printing technique developed by researchers from Harvard University: the rotational 3D printing method. This manufacturing process could revolutionize 3D printing by allowing to create stronger parts. How does it work? How will it help to print stiff and resistant 3D printed objects? All you need to know about rotational 3D printing is in this blog post.
What is rotational 3D printing?
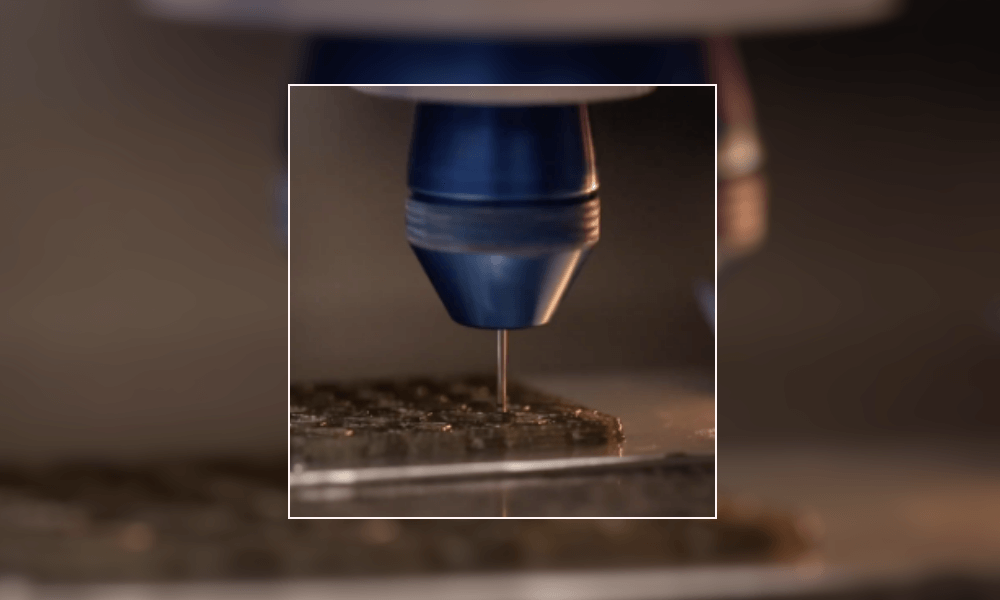
How does it work?
Researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) developed a 3D printing technique allowing to arrange short fibers inside of the 3D printing material. In order to do so, the printers head is spinning, that is why we call it rotational 3D printing.
What is the point of a spinning nozzle? This technique allows working on the position of the micro-fibers. It is a way to work on the microstructure of the parts to modify their properties. It could be the perfect solution to strengthen some parts of the object that you are creating, by modifying the complex microstructure of the materials.
A printing technique to reproduce natural mechanisms
Biologically inspired engineering has a lot to offer, and we must totally start to think about it. Rotational 3D printing is actually reproducing the same impressive mechanical properties and complex microstructures found in nature. This process is called biomimicry. The benefits and applications of biomimicry in the 3D printing industry are numerous and nature have much to teach us! Some mechanisms of nature can be applied to our manufacturing projects, copying structures and properties from nature composites.
It is clearly optimizing the properties of the material that we already use for additive manufacturing.
Advantages of this new printing technique
Using less material to get resistant parts
Controlling the fiber orientation is allowing to pattern the material, and create parts with a higher strength and stiffness. This process is a way to modify the microstructure and create new performances with the exact same material. It is a solution to increase the damage tolerance on some specific locations.
If the resistance of a material can be optimized using rotational 3D printing, it is making it totally possible to use less 3D printing material. It could become a money-saving printing technique, ensuring the quality and the resistance of the parts. The application of such a technique could be endless and improve a lot of projects.
“Rotational 3D printing can be used to achieve optimal, or near optimal, fiber arrangements at every location in the printed part, resulting in higher strength and stiffness with less material,” explains Brett Compton on of the researchers working on this study. “Rather than using magnetic or electric fields to orient fibers, we control the flow of the viscous ink itself to impart the desired fiber orientation.”
Actually, when we want to create really resistant parts, we have to use more and more material in order to strengthen the part where it is needed. Using rotational 3D printing opens new possibilities, and will allow developing new projects and new impressive structures.
Will it be possible to use this technique with any material?
One of the researchers on this project, Brett Compton, states that this 3D printing method could be on any material using the extrusion method. From direct ink writing to large-scale thermoplastic printing, and so on.
This additive manufacturing technique is really opening new possibilities and could lead to incredible 3D printing applications and experiments. This method could soon be available on a lot of different 3D printers.
Researchers are really understanding the huge potential of additive manufacturing and looking for new solutions to optimize its use and all of its capacities. Rotating 3D printing will definitely help to improve the development of additive manufacturing by creating projects always more impressive and qualitative, from mechanical engineering to architecture.
Do you want more blog posts about new 3D printing experiments? Subscribe to our newsletter right now!


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook