3D Printing Materials: Our Focus on Material Simulation.
Posted By Sculpteo on Mar 29, 2017 | 0 comments
Among the wide range of 3D printing materials that our online 3D printing service offers, you might not know which one to choose for your application, or have a clear idea of the properties of each one. Of course, you can always refer to our material pages, technical specifications, etc. But it can help also to have a comparison of unfamiliar 3D printing materials with more familiar materials that you encounter in your everyday life and in the industry. Some 3D printing materials “simulate” other, more familiar materials, and it’s this comparison that we want to provide today. After reading this article, we hope you will have more information to decide which material to choose for your 3D model, and which other material you can compare it to.
We put the materials into 4 big categories to differentiate them from each other: Plastics, Resins, Multicolor (composite material) and Metals. In this session, we will focus on the non-metal materials in order to understand what are the different properties of each 3D printing material and which other materials they can simulate.
1. Plastics
First, let’s start with the plastics, the most commonly used 3D printing materials according to the State of 3D Printing of 2016. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) technologies are mostly used to process plastic materials into 3D models. Relatively inexpensive, plastic still is the standard in 3D printing materials. The different materials properties in Plastics are:
Polyamide (PA)
3D Printed polyamide properties:
Commonly known as Nylon, this polyamide material is very strong. It is light and the smaller the wall thickness is, the more flexible it gets, which means you can also bend it. Applying the technology of Selective Laser Sintering, Polyamide is appropriate to create complex and delicate geometries. This material is relatively inexpensive and one of the toughest plastic materials.
It produces a rugous and slightly porous surface, but can then be polished, varnished or smoothed . Our smoothing beautifier finish for white polyamide makes 3D Printed polyamide parts very close to injection molding parts. It is also available for white parts dyed in black.
This material is relatively inexpensive and one of the toughest plastic materials. Our online 3D Printing service offers several colors of PA powder available: white plastic, solid black, and solid gray and so on. It can also be dyed or painted.
3D Printed polyamide applications:
3D Printed polyamide can be used to manufacture goods on a large scale, as you can see with the example of the NightQuest headphones by Audioquest, partly 3D printed.
Which other material can 3D printed polyamide “simulate”?
Polyamide has quite the same composition as most of the polymer materials which means PA can be an alternative solution to polymer materials such as Arcylonitrile Butadine Styrene (ABS), Polyester (PET), Acetals (POM) and many more.
ABS plastic (Arcylonitrile Butadine Styrene)
3D Printed ABS properties:
Part of the thermoplastic polymers family, this material is primarily used as filaments in FDM or FFF 3D printers that use material extrusion for its manufacturing process. Its advantages are its lightness and impact strength. ABS plastic can resist to temperature up to 200°C (392°F). In certain cases, ABS is biocompatible.
3D Printed ABS applications:
As FDM doesn’t create parts as strong as more industrial 3D printing techniques like SLS, ABS is mostly used for prototypes, and aspect parts.
Which other material can 3D printed ABS be compared to?
If you want to create the 3D model using another material with similar characteristics, polyamide can be used to imitate the ABS plastic. The differences: SLS usually creates stronger, more detailed parts, and Polyamide is more flexible than ABS. If your concern is to 3D printing an object that can resist higher temperatures, Cyanate Ester can be a solution, since it can resist up to 219°c .
PLA (Polyactic Acid)
3D Printed PLA properties:
PLA is a fully biodegradable thermoplastic that uses cornstarch as its special raw material. Using the technology of FDM, this vegetable-based material is slightly more fragile and less durable than other 3D printing materials.
3D Printed PLA applications:
As it has limited durability, Polyactic Acid is mostly used to create decorative objects without mechanical constraints.
Which other material can 3D printed PLA be compared to?
One of 3D printed PLA’s main competitor is ABS plastics. This Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a biocompatible material that can adapt and compatible to use with other technologies to create a 3D Printing objects. PLA is more biodegradable which its natural material is safer to use. However, it has a lower melting point than any other FDM materials around 150ºC which makes PLA is more sensitive to high temperature than ABS.
Alumide
3D Printed Alumide properties:
Using the SLS technology, Alumide has a mix composition between Polyamide 12 and Aluminium. Even though it has polyamide element which is very hard and solid, Alumide is more likely fragile and breakable under the massive loads.
3D Printed Alumide applications:
This mix material is very light and the aluminum gives metallic appearance on the surface of the objects making Alumide is better for prototyping or for figurines objects.
Which other materials can 3D printed Alumide be compared to?
Depending on the technologies used either Selective Laser Sintering or Fused Deposition Modeling, each of these techniques can propose different material properties to be simulated with Alumide. As an example, with the same technology SLS, Polyamide (Nylon) can simulate the details, texture and the solidity of alumide. On the other hand, you can also choose biocompatible material such as ABS Plastics to be compared.
Read: our Q&A about 3D Printing resolution on Alumide.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
3D Printed TPU properties:
TPU becomes one of the favorite material options for 3D flexible and elasticity prints. Use the SLS technology, this material is excellent for its flexibility and has layered textures but it is not as solid as the other polymer-based materials.The raw material looks off-white, grainy and porous. It has a rubber-like aspect, but slightly more silky. In our online 3D Printing Material, TPU can be found in several colors includes translucent and almost transparent as well.
3D Printed TPU applications:
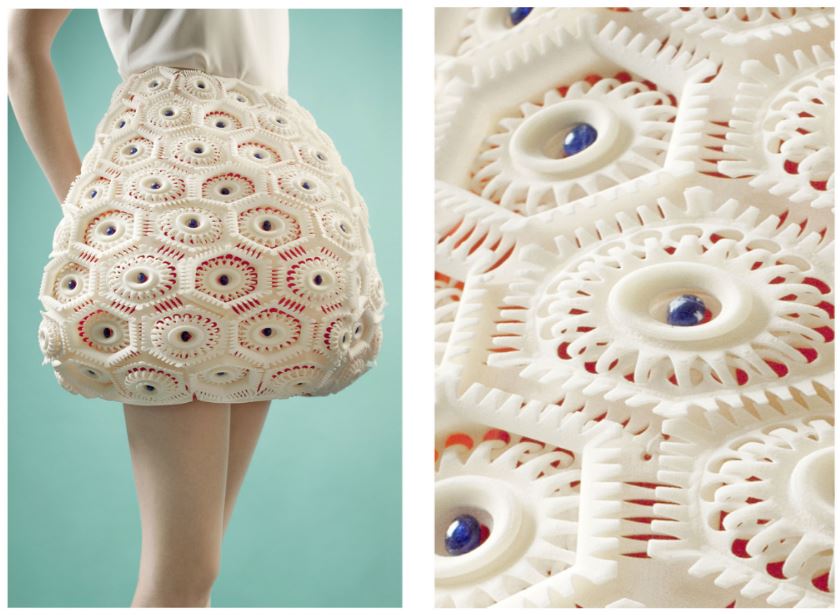
Our Flexible plastic has been used for several applications in medical industry to reproduce the organs to train the surgeons. Also for the fashion application which Anastasia Ruiz has been combining this TPU material into her Virus Collections. It can also be used for mechanical applications: prototyping, articulated objects and cases)
Read our article about 3D printing Flexible Plastic Material and Virus Collection
Which other material can 3D printed TPU be compared to?
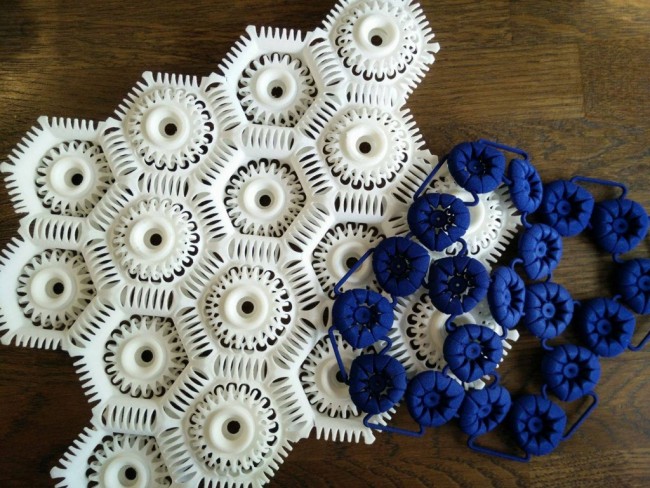
Taking an example of Virus Collection of Anastasia Ruiz, the project used two differents materials which was Polyamide and TPU to make different clothes. Both material share quite the same detail however TPU was used more in terms of layered and complex detail as these advantages gave the collection more flexible and gave more volume.
Virus collection 3D printed samples
Credits: Clausette.cc
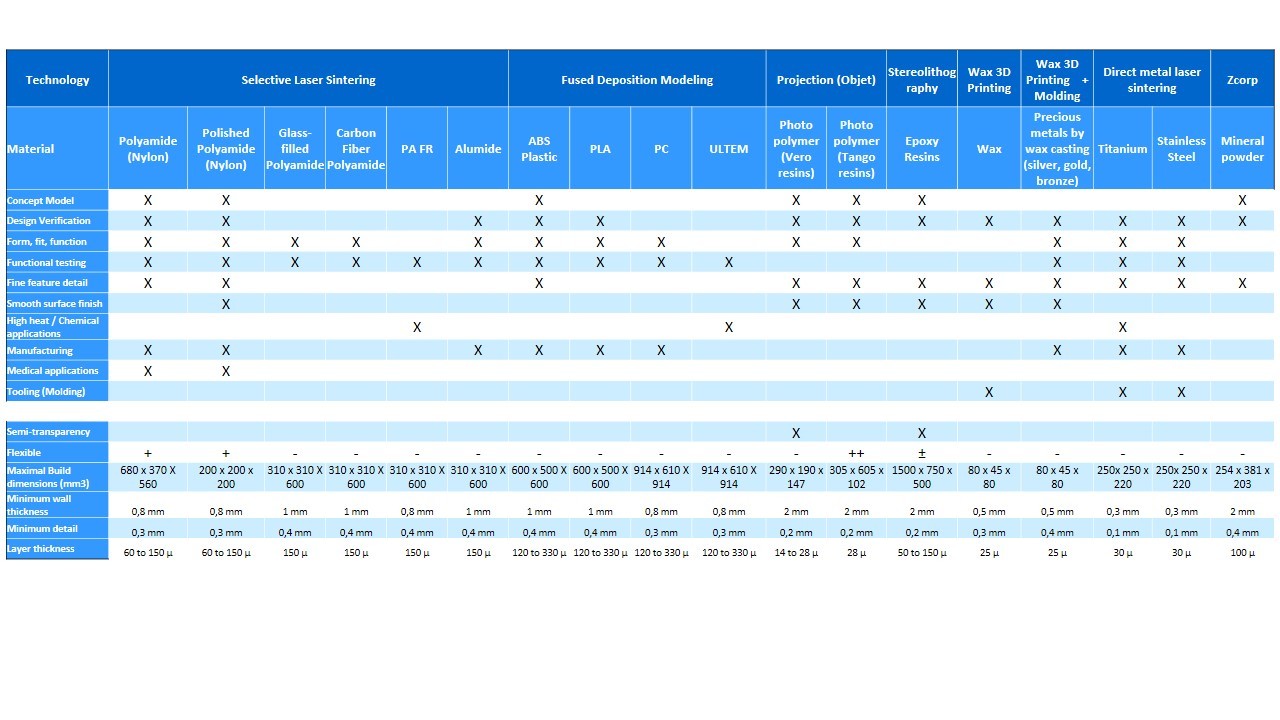
The table of different material above will show you more about which material for which use.
2. Resins
After plastics, resin is the most used material in 3D Printing particularly for the superior printing quality and maximum resolution which make resin is one of the excellent material for the professional applications. Resin materials use the multi technologies of SLA, Digital Light Processing (DLP), MultiJet or CLIP technologies to obtain fully creation of a 3D model. What are the resins material and what are the different properties of each of these materials:
Polyjet Resin.
3D Printed Polyjet Resin properties:
Our resin can create an object from the method of Stereolithography (SLA), based on the photopolymerization. The Polyjet resin enables to create detail and will result either white or translucent. The post-process colored will follow depending on the options chosen: Opaque, translucent and transparent.
3D Printed Polyjet Resin applications:
Polyjet Resin creates objects that are particularly detail and precise which are suitable for the ornamental objects and mechanical use (prototyping, designing end product).
Which other material can 3D printed TPU be compared to?
Translucent resin has a “frosted” appearance that makes it difficult to replicate with any other material without some sort of post-processing. However the
CLIP Resin.
Continuous Liquid Interface Production or is commonly known as CLIP, the 3D printing technology that consists of shaping the part by projecting a light through an oxygen-permeable window into a reservoir of UV-curable resin. Our CLIP resin is divided into four categories such as:
CE- Cyanate Ester
3D Printed Cyanate Ester properties:
Cyanate Ester, the material with a glass transition is remarkable for its resistance to high temperature which up to 219°C. Slightly rassemble to Rigid Polyurethane in terms of its solidity and weight, CE is a strong material that provides excellent thermal stability and useful for the industrial components and electronic applications.
3D Printed Cyanate Ester applications:
Marked by excellent strength, stiffness and long-term thermal stability, CE is useful for under-the-hood applications, electronics, and industrial components.
Read our Cyanate Ester Q&A article.
Which other material can 3D printed Cyanate Ester be compared to?
The polymer material of ABS plastics can simulate the Cyanate Ester. Although CE resists better than the ABS plastics, both share the similarity as they are safe to used within the demand application that requires high temperature.
RPU- Rigid Polyurethane
3D Printed RPU properties:
Rigid Polyurethane is prized for its solidity and resistance to strength. Based on photosensitive polymer liquid, RPU is very strong with material properties it is suitable for high resolution 3D prints, heat resistant and abrasion resistant.
3D Printed RPU applications:
This material is perfect for mechanical parts that need to be tough, heat-resistant, and abrasion-resistant.
Which other material can 3D printed RPU be compared to?
RPU characteristics outperform ABS plastic and rivals Polyamide which is known to be toughest plastic material. As we mentioned that resin enables to print on high resolution 3D model, using RPU resin will adding more precise detail and stiffness than Polyamide or ABS Plastic.
Prototyping Acrylate
3D Printed Prototyping Acrylate properties:
Based on photosensitive polymer, Prototyping Acrylate resin material creates 3D printed objects with smooth, lighter, solid and have shiny surface.
3D Printed Prototyping Acrylate applications:
This material is suitable for prototyping as it can 3D print incredible details.
Which other material can 3D printed Prototyping Acrylate “simulate”?
Prototyping Acrylate can be simulated with biocompatible ABS Plastic in terms of smoothness, fine details and
EPU- Elastomeric Polyurethane
3D Printed EPU properties:
EPU which is high-performance polyurethane elastomer is useful for applications that required high elasticity, impact and tear resistance. This material contains a very smooth and polishable texture. It is very solid and light and exhibit excellent elastic behaviour. EPU is using less material as there is no mold needed making the printing process is much faster than any other techniques such as FDM.
3D Printed EPU applications:
EPU is perfect for ornamental objects, but they can also be used for more mechanical uses if the strain on the object is not too great
Which other material can 3D printed EPU be “simulated” to?
This material can be compared to rubber as its texture is rassemble to the common material. Depending on the design, this rubber-like material EPU is hardly not tearable and you need more forces to tear object with EPU into pieces.
FPU- Flexible Polyurethane
3D Printed FPU properties:
Similar to its name, the material produces very good flexibility to stand for hard pressure. This CLIP resin material is a semi-rigid with good impact of abrasion and fatigue resistance. Designed to withstand repetitive stresses such as hinging mechanisms and friction fits, FPU creates final objects that are smooth on the outside and solid on the inside.
3D Printed FPU applications:
Flexible Polyurethane is an excellent 3D printing material, to 3D print objects for housewares, boxes and assemblies that need clipping, toys, rigid packaging, living hinges and everything that requires a lightweight and flexible plastic material.
Read: Flexible Polyurethane Material Q&A.
Which other material can 3D printed FPU be compared to?
However, do not mix the terms of ‘flexibility’ with the same material as EPU. Flexible Polyurethane is indeed flexible but it is not as rubber material like as EPU. Styrenes of polymers plastic (e.g. ABS) is likely to be simulated with FPU for the feature detail results.
3. Multicolor (composite material for 3D printing)
3D Printed Multicolor properties:
The multicolor 3D printing is formed using fine powdered material that resembles to sandstone. 3D print machine will apply directly the colors into the object which will also form the color combinations during the printing process. This multicolor 3D printing can be employed through three main 3D print technologies: Selective Deposition Lamination, ColorJet and the most used in our online 3D printing services in the Binder Jetting technology.
The printing process is quite similar to the SLS, except the powder grains are not aggregated with the heat of laser but with colored glues that applied locally through several printing heads that each supply one different colors: blue, red, yellow, black, white. With the machine ZCorp 3D Printer that we use, the combination of colored glues creates up to 390.000 colors possibilities.
3D Printed Multicolor applications:
Multicolor is the perfect material for figurines, avatars, 3D-scans and anything that require full 3D print color.
Read our recent article about “Multicolor 3D printing: How does it work and What is it for?”
Which other material can 3D printed Multicolor be compared to?
Light and also fragile, multicolor material can break so easily, multicolor objects are comparable to ceramic material or porcelain.
You can go to our business case platform where you can estimate your 3D project and have suggestions about materials choices you may use, the 3D designs/files, pricing and process time.


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook